Adulterant Information
Adulterants are reagents that are contained on a test strip to help aid in the detection of urine tampering. The adulterant test strips contain chemically treated reagent pads which change colors and are designed to help assess the integrity of the urine specimen. "Adulteration" is the tampering of a urine specimen by the donor with the intention of altering the test results. If the donor is successful, the use of adulterants in the urine specimen can cause false negative results by interfering with the test and destroying the drugs present in the urine. "Dilution" is another method the donor may use to produce false negative drug test results. Determining certain urinary characteristics such as specific gravity (SG), and pH and to detect the presence of oxidants (OX), glutaraldehyde, nitrite, and creatinine in the specimen are considered to be the best ways to test for adulteration or dilution.
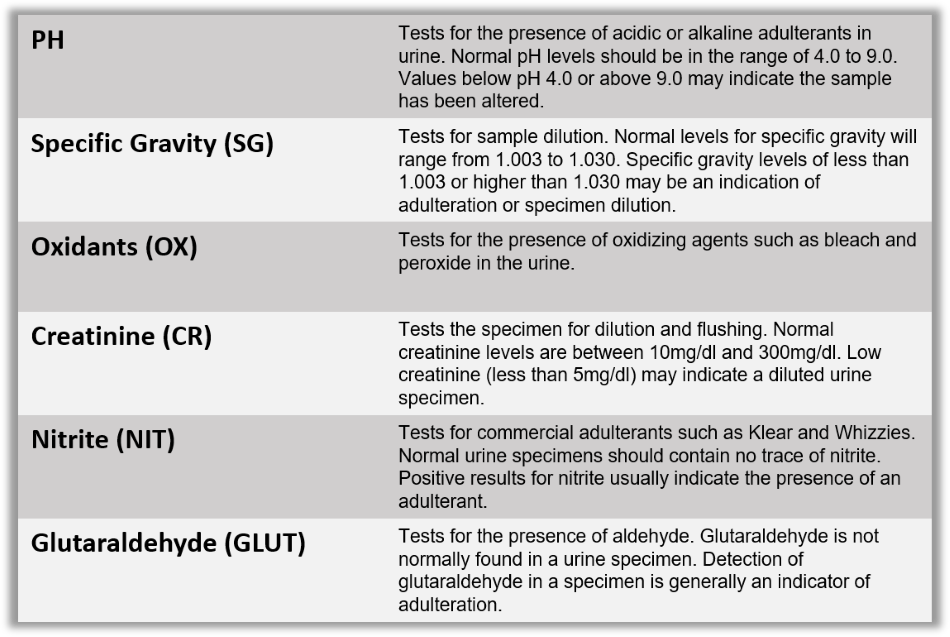
How Do You Read An Adulterant Strip?
Specimens that have not been adulterated will display a normal color range on the pad. Abnormal results (high or low) require collection of a new specimen and re-testing. Read the adulterant strip at 1 minute.

